“Can We Live in Coexistence?: Turkiye’s Refugee Issue”
“Can We Live in Coexistence?: Turkiye’s Refugee Issue”

By Turkiye Report
June 2022
As of 2011, as a result of the exacerbation of the libertarian movements brought by the Arab Spring in Syria, a more visible refugee population has emerged within the borders with the wave of immigration flowing to Turkey. Perhaps many people, who now openly define themselves as anti-refugee, approached the “brothers of religion” that we temporarily hosted at the time, with the admiration of the coexistence of different cultures. It is undeniable that these negative developments in the economic field such as the increase in food prices, the rent problem, the record increase in housing prices, and unemployment, triggered the opposition to asylum seekers. However, it would be an incomplete perspective to reduce the refugee problem to economic reasons. Refugees, who are no longer a small minority in the demographic structure of the country, are more visible with the increase in their numbers and are no longer just lost in the crowd of Fatih district. The presence of Syrians, Pakis and Afghans in social areas in almost every district of Istanbul is the focus of the most current social debates.
Social media has become an environment where those who think that asylum seekers cause internal security problems do not filter their thoughts. Victory Party Chairman Ümit Özdağ, who made an important breakthrough by expressing the problems created by the refugees, increased his political visibility and received an important response in the society. on the other hand, indicates that the tolerant approach towards refugees has disappeared. “How Open Are We to Differences?”, which we conducted as the Turkey Report in February 2021. In the survey, those who said that they did not agree with the statement “Having a Syrian neighbor makes me uncomfortable” comprised the majority of 59%. In our survey in May, in which we discussed the refugee problem, 79% said that refugees have a domestic security problem. This change, which has taken place over a year, draws attention. In our May report, we discussed the refugee problem with its social and economic dimensions and analyzed it for you with various breakdowns.
Which of the following statements do you agree with regarding the effects of refugees/asylum seekers in Turkey on political and social life? (%)
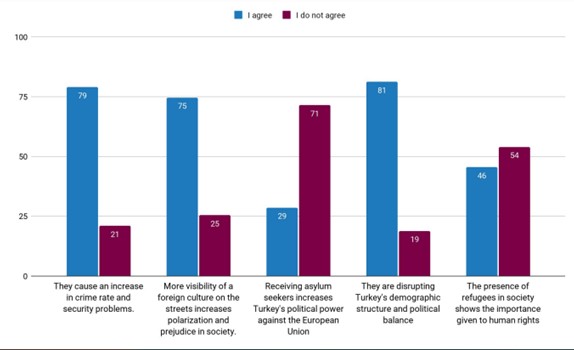
When the participants are asked about the effects of asylum seekers in political and social life, a negative perspective is generally encountered against asylum seekers. While 80% of the participants reported that asylum seekers cause an increase in crime rate and security problems, 75% state that the presence of a foreign culture on the streets increases polarization and prejudice in the society. Those who say that asylum seekers disrupt Turkey’s demographic structure and political balance still make up the 81% majority. Those who argue that accepting asylum seekers increases Turkey’s political power against the EU are in the minority with 29%. The rate of those who say that the presence of refugees in the society shows the importance given to human rights is determined as 46%.
Which of the following statements about the effects of refugees in Turkey on economic life do you agree with? (%)
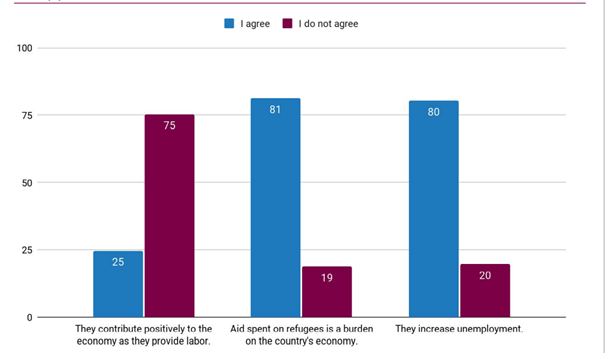
We asked our participants to evaluate some of the statements we have listed about the effects of refugees on economic life in Turkey. After the survey we conducted, we concluded that the majority evaluated the effects of refugees on economic life negatively. A significant majority with 81% of those who participated in the survey think that the aid spent on refugees creates a burden on the country’s economy. While 80% of the respondents thought that refugees caused an increase in unemployment, only 25% agreed with the statement that “they make a positive contribution to the economy as they provide labor”
When we examine the results within the framework of the working status of the participants, we see that the majority of all groups think that refugees are one of the reasons for the increase in unemployment.The highest rate of those expressing this view belongs to the students with 91%. 89% of our respondents who are unemployed and looking for a job also establish a relationship between the increase in unemployment and refugees. It is known that refugees are seen as “cheap labor” due to their fragile status in Turkish society and are employed unregistered. However, the results point to another striking data: According to the people who are currently unemployed and looking for a job, one of the reasons for unemployment is the existence of refugees. Therefore, it can be said that refugees are being targeted as the cause of current economic problems including unemployment. While the rates are close between people from different employment status, we see that approximately 29% of employers think that refugees do not cause an increase in unemployment. This rate is around 27% among paid government employees. The rate of those who think that refugees cause unemployment increases in groups working for the state or doing their own business, compared to groups working in a company or unemployed.